Metaspolit is a very powerful tool that will allow you to exploit certain vulnerabilities within target machines. It comes already installed on Kali Linux, but there’s a few things you need to do at the command line before you can get started.
PREREQUISITES
- You should have a Linux Live drive boot already
- You should have a connection to a LAN or WAN
- Know the IP address range of the network you are targeting
In this tutorial we will be exploiting the afp module for a macintosh computer running on our LAN. We will use the afp_server_info module in metasploit to find out more details about our target machine.
STEP 1
The first step is to find out information about our target network. Run an arp scan on the network you are targeting. with the following command
arp-scan 192.168.0.1/24
You can change the IP address range to match the network you wish to scan. After running this you will be presented with all the devices connected to the network.
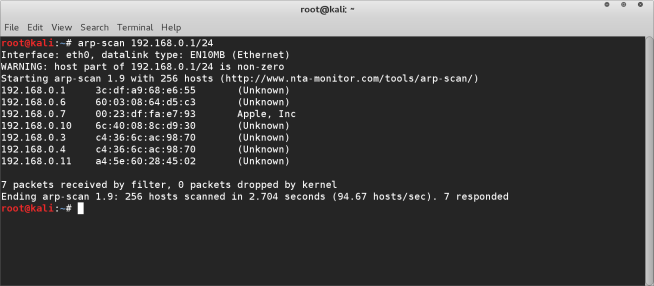 You can see that we have several devices connected to our network.
You can see that we have several devices connected to our network.
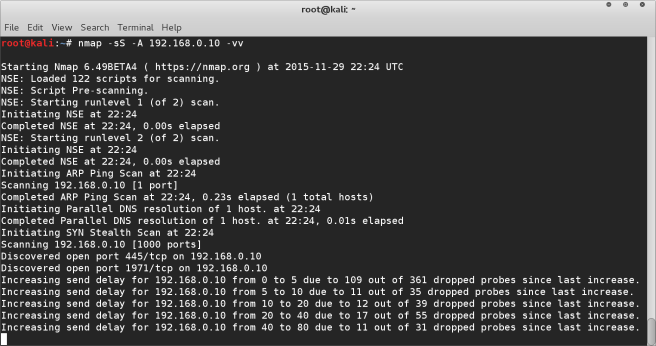
Next we will find out what services and ports are open on which machines using nmap :-
nmap -sS -A 192.168.0.1/24 -v

After running this scan you will be able to look at the results and identify the IP address of a machine that has several open ports. These open ports are what we will use to exploit, so the more ports a specific machine has open the better. Once you have identified this we will run one final scan on the specific target machine :-
nmap -sS -A 192.168.0.10 -vv
STEP 2
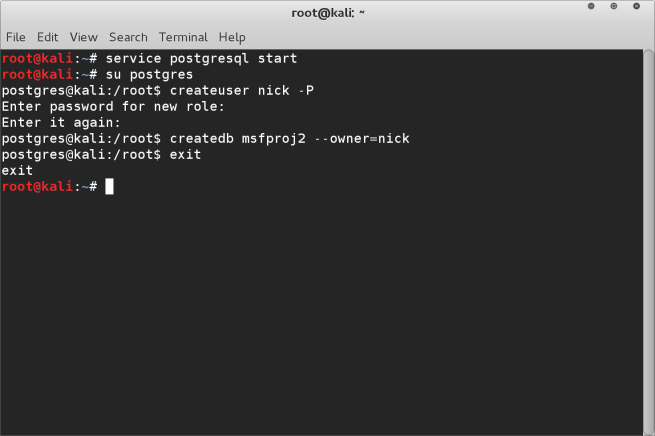
Now we have identified our target machine we can setup our database which will be used by metasploit. Open up a new terminal window and run the following :-
service postgresql start
su postgres
createuser nick -P
createdb msfproj2 –owner=nick
exit
(choose your own username and database name and password)
STEP 3
Now we are ready to start the metasploit program by running the msfconsole command
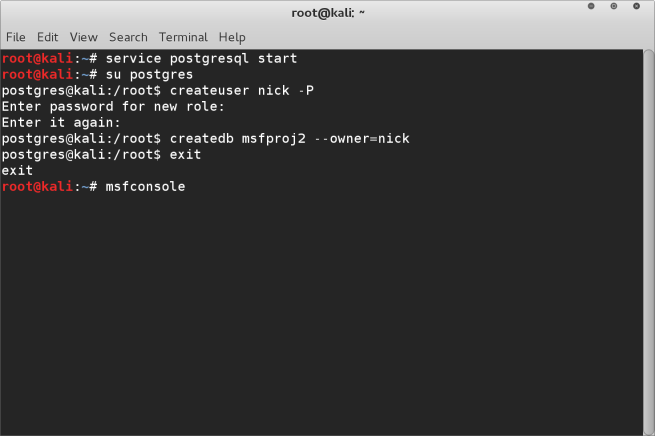
Once msfconsole is loaded, we need to connect to the database we just created.
db_disconnect
db_connect nick:<your password>@localhost/<your db name>
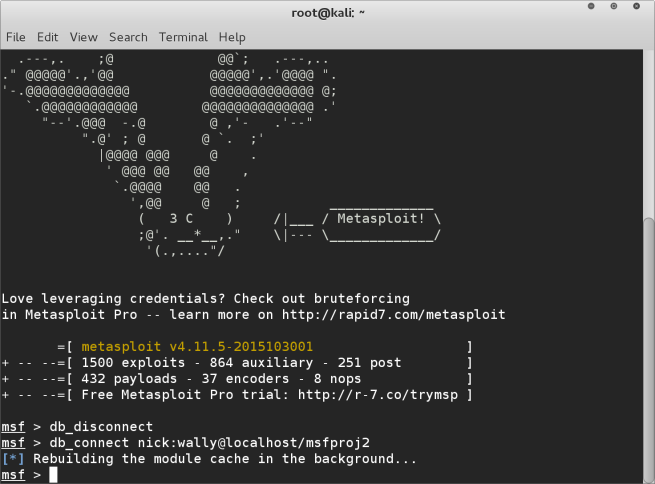
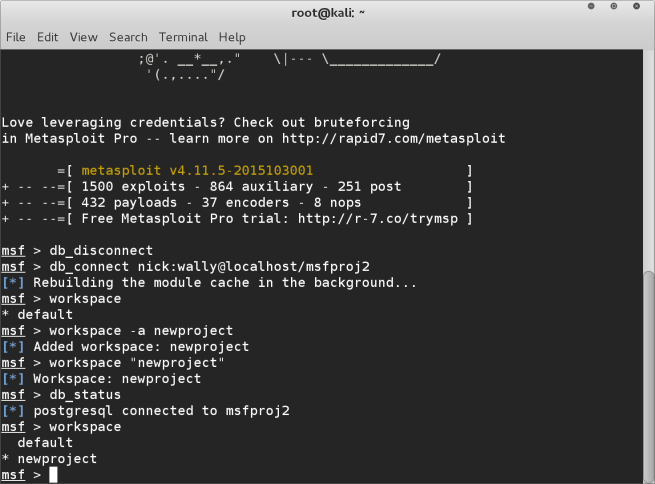
Now we need to setup a new workspace.
workspace -a newproject
workspace “newproject”
To check that everything is setup properly run :-
db_status
workspace
The results of these two commands should show that your postgresql is connected to the correct database.
STEP 4
Now we have metaspoilt setup and connected to our database we can run nmap again on our target network, but this time it will write the results to be saved into the database :-
db_nmap -sS 192.168.0.1/24 -vv
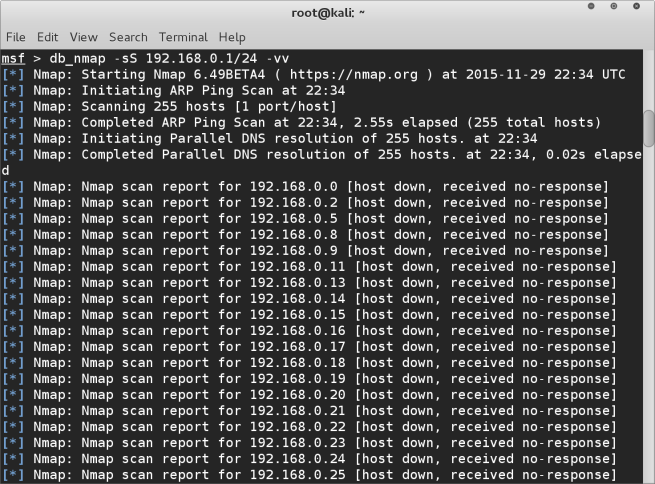
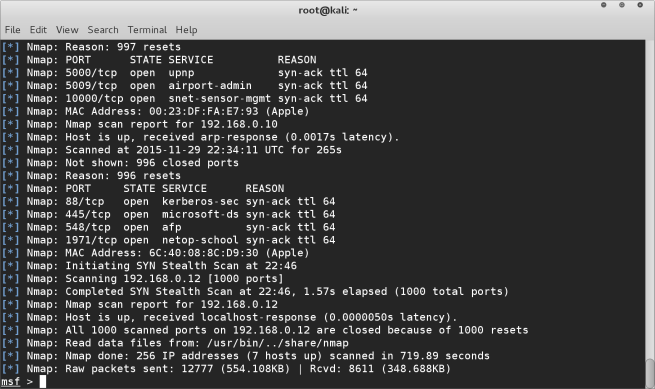
Once the scan is complete we can run the command hosts to be shown a list of devices connected to the network.
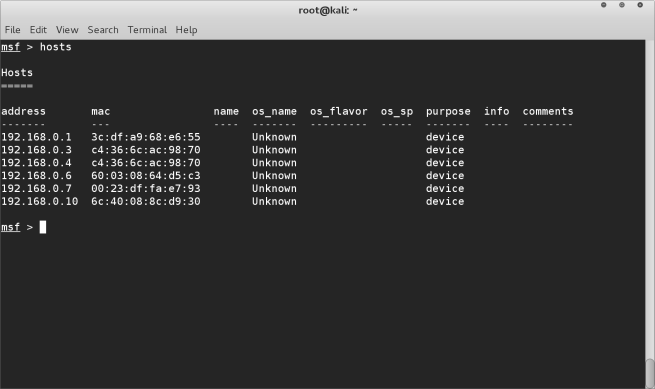
the services command will display all the services that are running on the network which we can exploit. When you find a service you want to exploit, you can check if metaspoilt has any exploits for this service by using the search <service name> command
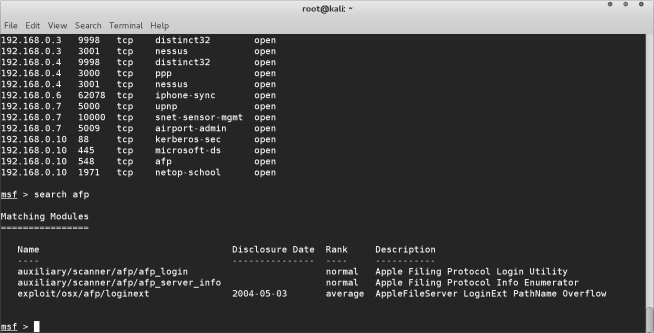
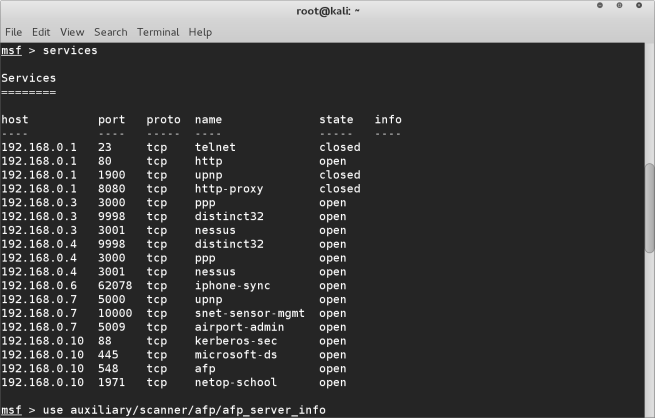
In this case we have identified the afp service that we wish to exploit. There are several modules for afp that we can use. We are going to do a very basic “attack” to gain more information about the computer on the network.
use auxiliary/scanner/afp/afp_server_info
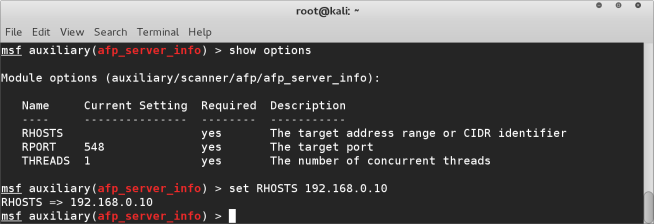
after loading this module, we need to view the options. show options command will do this for us. You can see that it also lists which of these options are mandatory under the “required” column. In the case of the afp_server_info module all options are required. Two are already filled in by default. Check that the port matches the port that was listed under the services list. If this is already setup OK, we only ned to add RHOSTS which will be the IP address of the target machine, of a range of IP addresses. We are targeting machine 192.168.0.10 so we will run the command set RHOSTS 192.168.0.10
We are now finally ready to run the module, simply use the command run or exploit and the module will run giving it’s results as shown below.
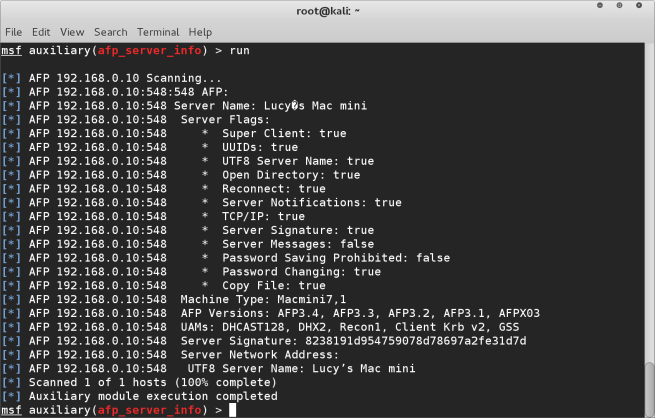
The above shows details about our target machine, it’s network/server name, the type of machine etc. This information can be useful for us when planning further penetration attacks on this machine.
SUMMARY
So that’s a very brief and basic introduction to metasploit framework. It covers just a fraction of what this very powerful program is capable of doing. In later tutorials we will be going deeper into metasploit and what it can do. In the next tutorial we will be doing another function with the afp exploit to crack the password for the user.