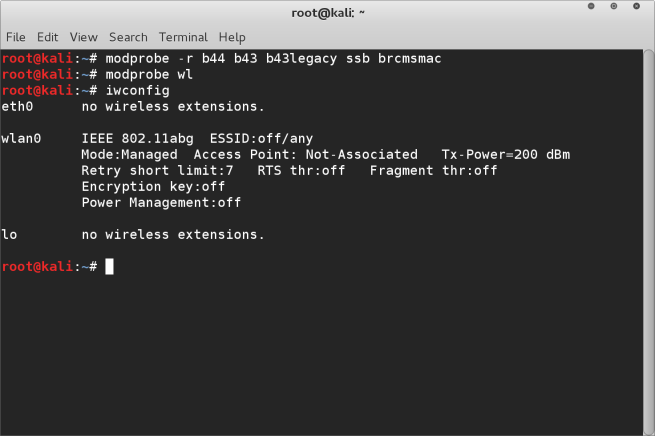
One headache people often come across when setting up wireless cards on their macbook with Linux apart from actually getting it working (see this post for help on that) is enabling monitoring mode.
By default the broadcom drivers don’t allow the wireless network card in the macbook (and I assume other Mac variants) to be put into monitor mode. This is particularly frustrating when you need to run airodump-ng for example to capture wireless packets.
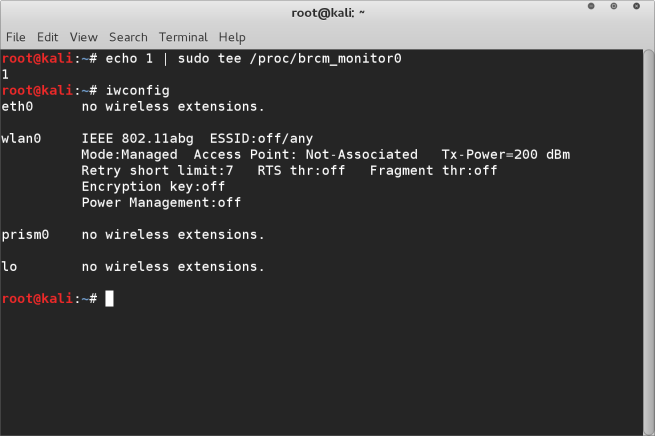
There is however a solution for this that I have discovered, you simply need to execute the following command at the terminal
echo 1 | sudo tee /proc/brcm_monitor0
After this if you run the ifconfig command you will see a new wireless device is listed prism0. This is your monitoring device for your wireless card. So when you run airodump-ng for example, rather than using mon0 as the interface you will substitute it for prism0
To test this is working run airodump-ng prism0 command in the terminal. You should then see the wireless networks and the packets being collected like this :-
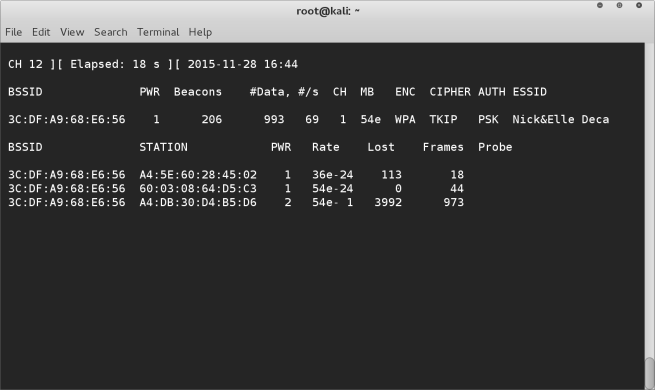
And there you have it, your broadcom wireless card on a macbook pro 2014 model up and running with monitor mode enabled. Enjoy!
Note, you will need to run this terminal command to setup prism0 after each reboot, even with persistence enabled.